Question 53
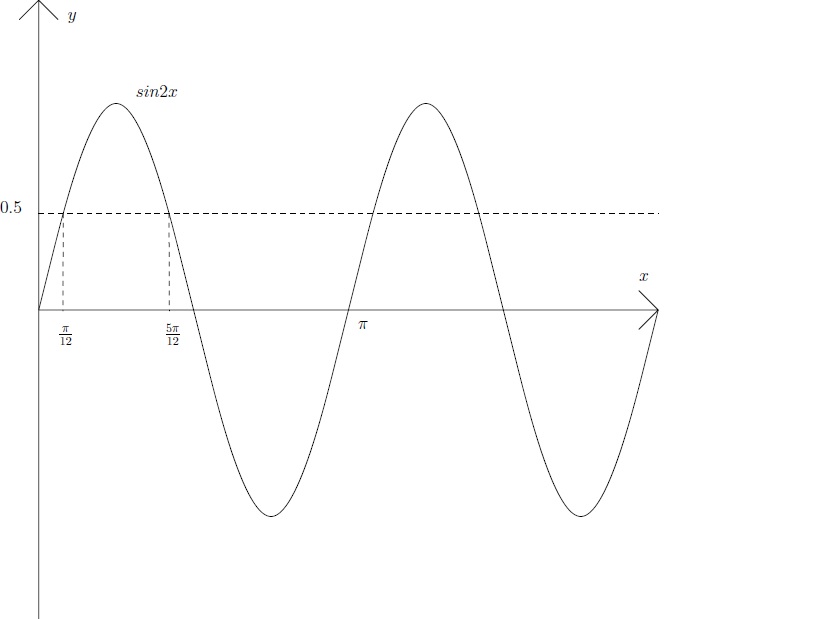
The first inequality yields $0\leq x\leq\frac{\pi}{4}$ or $\frac{3\pi}{4}\leq x \leq\pi$ and the second inequality achieves equality when $2x=\frac{\pi}{6}$ or $\frac{5\pi}{6}$ therefore $x=\frac{\pi}{12}$ or $\frac{5\pi}{12}$. This inequality is satisfied for $\frac{\pi}{12} \leq x \leq \frac{5\pi}{12}$.
Both inequalities are satisfied for $\frac{\pi}{12} \leq x \leq \frac{\pi}{4}$ and $\frac{\pi}{4}-\frac{\pi}{12}=\frac{\pi}{6}$.
The first inequality yields $0\leq x\leq\frac{\pi}{4}$ or $\frac{3\pi}{4}\leq x \leq\pi$ and the second inequality achieves equality when $2x=\frac{\pi}{6}$ or $\frac{5\pi}{6}$ therefore $x=\frac{\pi}{12}$ or $\frac{5\pi}{12}$. This inequality is satisfied for $\frac{\pi}{12} \leq x \leq \frac{5\pi}{12}$.
Both inequalities are satisfied for $\frac{\pi}{12} \leq x \leq \frac{\pi}{4}$ and $\frac{\pi}{4}-\frac{\pi}{12}=\frac{\pi}{6}$.